Appearance
RADIUS Setup Guide
Overview
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) is the industry-standard protocol for AAA (Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting) in ISP networks. Zal Ultra includes a built-in FreeRADIUS server that handles all authentication and accounting for PPPoE, Hotspot, and other services.
What is RADIUS?
RADIUS = Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service
✅ Industry standard (RFC 2865, RFC 2866)
✅ Authentication (verify username/password)
✅ Authorization (assign IP, bandwidth, expiry)
✅ Accounting (track usage, session time, data)
✅ Supports PPPoE, Hotspot, VPN, 802.1X
✅ Vendor-neutral protocolHow RADIUS Works:
1. User connects (PPPoE/Hotspot)
2. NAS (router) sends Access-Request to RADIUS
3. RADIUS validates credentials in database
4. RADIUS sends Access-Accept with attributes
5. NAS creates session and assigns IP/bandwidth
6. NAS sends Accounting-Start to RADIUS
7. NAS sends Interim-Update periodically
8. RADIUS tracks usage and enforces quotas
9. NAS sends Accounting-Stop when session endsTable of Contents
- MikroTik RADIUS Setup
- Zal Ultra Built-in RADIUS
- FreeRADIUS Installation
- RADIUS Attributes
- CoA (Change of Authorization)
- Troubleshooting
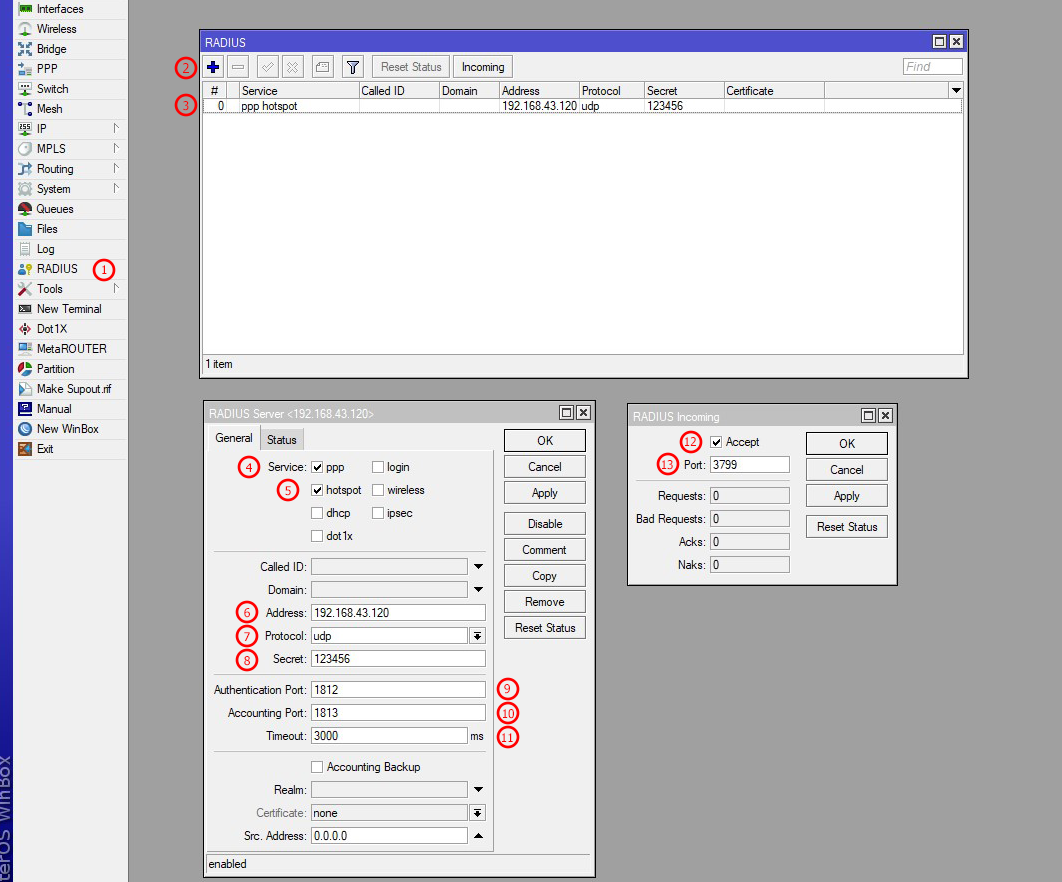
MikroTik RADIUS Setup
Configure RADIUS Server
| Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | First, go to the Radius module in Mikrotik from the left sidebar menu |
| 2 | From the new window, create a new Radius Server by clicking on the plus button. A new window will appear as Radius Server for Radius Setups |
| 3 | Open it once the radius service is created |
| 4 | From the new Radius Server window, select the General tab from the top bar and select the PPP service for PPP auth request and accounting |
| 5 | From the new Radius Server window, select the General tab from the top bar and select the Hotspot service for Hotspot auth request and accounting |
| 6 | Enter your Radius Server IP address here. Mikrotik will send PPP and Hotspot requests to this Radius Server (Zal Ultra) for Radius Auth and Accounting |
| 7 | Select Default Radius Protocol UDP |
| 8 | Insert your Radius Server NAS secret here. You must insert the same NAS secret as you inserted in Zal Ultra Network → NAS module. Warning: If you don't insert the same NAS secret, users will not connect at all. You can't use any special characters here; only plain text/letters/words/numbers will work. If you face any issues, like users not connecting or users being accepted in Zal Ultra but not connecting in Mikrotik, or if the user's connection drops after a few seconds, recheck your Zal Ultra NAS secret and this NAS secret. Both secrets must match. If you still face issues, set the secret to 123456, which will work for any NAS in your network |
| 9 | Set the Authentication port to 1812 for the Radius Server. Do not change these ports; use the default port as it is. If you want/need to change the port, then contact us |
| 10 | Set the Accounting port to 1813 for the Radius Server. Do not change these ports; use the default port as it is. If you want/need to change the port, then contact us |
| 11 | Very important radius timeout time, set Timeout to 3000 milliseconds. Do not set lower or higher than this |
| 12 | You must enable Radius Incoming requests from the Radius Server (Zal Ultra) for CoA (Change of Authorization). Zal Ultra uses this feature to change user bandwidth limits or to disconnect users from Mikrotik/NAS |
| 13 | You must set Radius Incoming port for CoA (Change of Authorization), and both CoA ports should match in Zal Ultra NAS settings and here. The default is 3799. If CoA is not enabled, Zal Ultra can't disconnect users from Mikrotik when needed. Zal Ultra only sends disconnect and bandwidth changing requests to the user-connected NAS/IP/Mikrotik. You must set the correct NAS/Mikrotik/IP to the user in the user profile. If the connected user's IP does not match properly or if your Radius secret does not match with Zal Ultra NAS Radius secret, you will see errors here as NAKS |
CLI Command:
bash
# Add RADIUS server (Zal Ultra)
/radius
add service=ppp,hotspot \
address=192.168.1.100 \
secret=YourSecretKey123 \
authentication-port=1812 \
accounting-port=1813 \
timeout=3000ms \
src-address=192.168.1.1 \
comment="Zal Ultra RADIUS Server"
# Enable CoA (Change of Authorization)
/radius incoming
set accept=yes port=3799RADIUS Ports:
| Port | Protocol | Purpose | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1812 | UDP | Authentication | RFC 2865 |
| 1813 | UDP | Accounting | RFC 2866 |
| 3799 | UDP | CoA (Dynamic Authorization) | RFC 5176 |
⚠️ CRITICAL: RADIUS Secret
The RADIUS secret is the shared password between NAS and RADIUS server.
Requirements:
✅ MUST match exactly on both sides
✅ Case-sensitive
✅ No leading/trailing spaces
✅ Avoid special characters (use alphanumeric only)
✅ Minimum 8 characters recommended
✅ Maximum 128 characters
If secrets don't match:
❌ Authentication will ALWAYS fail
❌ Users cannot connect
❌ No helpful error message
❌ RADIUS shows "Access-Reject"
❌ NAS shows "authentication failed"
Troubleshooting:
1. Check MikroTik: /radius print detail
2. Check Zal Ultra: Network → NAS → View NAS
3. Ensure exact match (copy-paste recommended)
4. Test with simple secret like "123456" first
5. Check for hidden characters or spacesZal Ultra Built-in RADIUS
What is Included
Zal Ultra includes FreeRADIUS 3.x with:
✅ MySQL/MariaDB backend
✅ PPPoE authentication
✅ Hotspot authentication
✅ Real-time accounting
✅ CoA support
✅ Bandwidth control via RADIUS attributes
✅ IP pool management
✅ Session management
✅ Quota enforcementHow Zal Ultra Uses RADIUS
Authentication Flow:
1. User connects (PPPoE/Hotspot)
2. NAS sends Access-Request to Zal Ultra RADIUS
3. Zal Ultra checks:
- Username exists?
- Password correct?
- Package active?
- Expiry date valid?
- Quota remaining?
4. If valid: Send Access-Accept with:
- Framed-IP-Address (user IP)
- Mikrotik-Rate-Limit (bandwidth)
- Session-Timeout (expiry)
- Other attributes
5. If invalid: Send Access-RejectAccounting Flow:
1. Session starts → Accounting-Start
- Record session start time
- Store NAS IP, username, session ID
2. During session → Interim-Update (every 3-5 min)
- Update data usage (upload/download)
- Check quota limits
- Enforce bandwidth
3. Session ends → Accounting-Stop
- Record session end time
- Final data usage
- Calculate charges
- Update databaseFreeRADIUS Installation
Install FreeRADIUS (Standalone)
For Ubuntu/Debian:
bash
# Update system
apt-get update
apt-get upgrade -y
# Install FreeRADIUS and MySQL module
apt-get install -y freeradius freeradius-mysql freeradius-utils
# Install MariaDB
apt-get install -y mariadb-server mariadb-client
# Secure MariaDB
mysql_secure_installationFor CentOS/RHEL:
bash
# Install FreeRADIUS
yum install -y freeradius freeradius-mysql freeradius-utils
# Install MariaDB
yum install -y mariadb-server mariadb
# Start and enable services
systemctl start mariadb
systemctl enable mariadb
systemctl start radiusd
systemctl enable radiusdConfigure FreeRADIUS Database
bash
# Create RADIUS database
mysql -u root -p << 'EOF'
CREATE DATABASE radius;
GRANT ALL ON radius.* TO 'radius'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'radiuspass';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
EXIT;
EOF
# Import RADIUS schema
mysql -u radius -p radius < /etc/freeradius/3.0/mods-config/sql/main/mysql/schema.sqlConfigure FreeRADIUS
1. Enable SQL Module
bash
# Link SQL module
cd /etc/freeradius/3.0/mods-enabled
ln -s ../mods-available/sql sql
# Edit SQL configuration
nano /etc/freeradius/3.0/mods-available/sqlSQL Configuration:
sql {
driver = "rlm_sql_mysql"
dialect = "mysql"
server = "localhost"
port = 3306
login = "radius"
password = "radiuspass"
radius_db = "radius"
read_clients = yes
client_table = "nas"
pool {
start = 5
min = 4
max = 32
spare = 3
uses = 0
lifetime = 0
idle_timeout = 60
}
}2. Configure Clients (NAS)
bash
# Edit clients.conf
nano /etc/freeradius/3.0/clients.confAdd NAS:
client mikrotik-1 {
ipaddr = 192.168.1.1
secret = YourSecretKey123
shortname = mikrotik-1
nastype = mikrotik
}
client mikrotik-2 {
ipaddr = 192.168.1.2
secret = YourSecretKey123
shortname = mikrotik-2
nastype = mikrotik
}
# Or allow entire subnet
client private-network {
ipaddr = 192.168.1.0/24
secret = YourSecretKey123
shortname = private-net
}3. Configure RADIUS Attributes
bash
# Edit dictionary
nano /etc/freeradius/3.0/dictionaryAdd MikroTik VSA:
# MikroTik Vendor Specific Attributes
VENDOR Mikrotik 14988
BEGIN-VENDOR Mikrotik
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Recv-Limit 1 integer
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Xmit-Limit 2 integer
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Group 3 string
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Wireless-Forward 4 integer
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Wireless-Skip-Dot1x 5 integer
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Wireless-Enc-Algo 6 integer
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Wireless-Enc-Key 7 string
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Rate-Limit 8 string
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Realm 9 string
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Host-IP 10 ipaddr
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Mark-Id 11 string
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Advertise-URL 12 string
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Advertise-Interval 13 integer
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Recv-Limit-Gigawords 14 integer
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Xmit-Limit-Gigawords 15 integer
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Wireless-PSK 16 string
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Total-Limit 17 integer
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Total-Limit-Gigawords 18 integer
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Address-List 19 string
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Wireless-MPKey 20 string
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Wireless-Comment 21 string
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Delegated-IPv6-Pool 22 string
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-DHCP-Option-Set 23 string
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-DHCP-Option-Param-STR1 24 string
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-DHCP-Option-Param-STR2 25 string
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Wireless-VLANID 26 integer
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Wireless-VLANIDtype 27 integer
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Wireless-Minsignal 28 string
ATTRIBUTE Mikrotik-Wireless-Maxsignal 29 string
END-VENDOR Mikrotik4. Start FreeRADIUS
bash
# Test configuration
freeradius -X
# If no errors, start service
systemctl start freeradius
systemctl enable freeradius
# Check status
systemctl status freeradiusRADIUS Attributes
Standard RADIUS Attributes
| Attribute | Type | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| User-Name | String | Username | user001 |
| User-Password | String | Password | password123 |
| NAS-IP-Address | IP | NAS router IP | 192.168.1.1 |
| NAS-Port | Integer | Physical port | 0 |
| Service-Type | Integer | Service type | 2 (Framed) |
| Framed-Protocol | Integer | Protocol | 1 (PPP) |
| Framed-IP-Address | IP | Assigned IP | 10.10.1.100 |
| Framed-IP-Netmask | IP | Netmask | 255.255.255.255 |
| Framed-Route | String | Static route | 192.168.2.0/24 |
| Filter-Id | String | Filter/Policy | premium-user |
| Session-Timeout | Integer | Max session time (sec) | 86400 (24h) |
| Idle-Timeout | Integer | Idle timeout (sec) | 600 (10min) |
| Called-Station-Id | String | NAS identifier | ISP-PPPoE |
| Calling-Station-Id | String | Client MAC | 00:11:22:33:44:55 |
| NAS-Identifier | String | NAS name | mikrotik-main |
| Acct-Status-Type | Integer | Accounting type | 1 (Start), 2 (Stop) |
| Acct-Input-Octets | Integer | Bytes received | 1048576 |
| Acct-Output-Octets | Integer | Bytes sent | 5242880 |
| Acct-Session-Id | String | Unique session ID | 80000001 |
| Acct-Session-Time | Integer | Session duration (sec) | 3600 |
| Acct-Terminate-Cause | Integer | Disconnect reason | 1 (User-Request) |
MikroTik Vendor Specific Attributes (VSA)
| Attribute | ID | Type | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mikrotik-Rate-Limit | 8 | String | Bandwidth limit | 10M/10M |
| Mikrotik-Group | 3 | String | User group | premium |
| Mikrotik-Address-List | 19 | String | Firewall address list | allowed-users |
| Mikrotik-Recv-Limit | 1 | Integer | Download limit (bytes) | 1073741824 (1GB) |
| Mikrotik-Xmit-Limit | 2 | Integer | Upload limit (bytes) | 1073741824 (1GB) |
| Mikrotik-Advertise-URL | 12 | String | Advertisement URL | http://ads.isp.com |
| Mikrotik-Advertise-Interval | 13 | Integer | Ad interval (sec) | 300 (5min) |
Mikrotik-Rate-Limit Format:
Format: rx-rate[/tx-rate] [rx-burst-rate[/tx-burst-rate] [rx-burst-threshold[/tx-burst-threshold] [rx-burst-time[/tx-burst-time] [priority] [rx-rate-min[/tx-rate-min]]]]
Examples:
10M/10M → 10 Mbps download/upload
20M/5M → 20 Mbps down, 5 Mbps up
10M/10M 20M/20M 5M/5M 8/8 → With burst
512k/128k → 512 Kbps down, 128 Kbps upCoA (Change of Authorization)
What is CoA?
CoA = Change of Authorization (RFC 5176)
Also known as: Dynamic Authorization, RADIUS Disconnect
Purpose:
✅ Disconnect user remotely
✅ Change session attributes (bandwidth, IP, etc.)
✅ Force re-authentication
✅ Update quotas in real-time
CoA Request Types:
1. Disconnect-Request: Terminate session
2. CoA-Request: Change session attributesEnable CoA on MikroTik
bash
# Enable RADIUS incoming (CoA)
/radius incoming
set accept=yes port=3799
# Verify
/radius incoming printCoA from Zal Ultra
When Zal Ultra Sends CoA:
1. User quota exceeded
→ Send Disconnect-Request
2. Package upgraded/downgraded
→ Send CoA-Request with new Mikrotik-Rate-Limit
3. User expired
→ Send Disconnect-Request
4. Manual disconnect by admin
→ Send Disconnect-Request
5. Bandwidth change
→ Send CoA-Request with new rate limitTest CoA Manually
bash
# Install radclient
apt-get install -y freeradius-utils
# Disconnect user
echo "User-Name=user001" | \
radclient 192.168.1.1:3799 disconnect YourSecretKey123
# Change bandwidth
echo "User-Name=user001,Mikrotik-Rate-Limit=20M/20M" | \
radclient 192.168.1.1:3799 coa YourSecretKey123Troubleshooting
Issue 1: Authentication Fails
Symptoms:
❌ User cannot connect
❌ "Authentication failed" error
❌ RADIUS shows "Access-Reject"Diagnosis:
bash
# Test RADIUS authentication
radtest username password 192.168.1.100 0 YourSecretKey123
# Check RADIUS logs
tail -f /var/log/freeradius/radius.log
# Debug mode
freeradius -X
# Check database
mysql -u radius -p radius
SELECT * FROM radcheck WHERE username='user001';Common Causes:
1. Wrong password
Solution: Verify password in database
2. RADIUS secret mismatch
Solution: Check NAS secret matches clients.conf
3. User not in database
Solution: Add user to radcheck table
4. FreeRADIUS not running
Solution: systemctl start freeradius
5. Firewall blocking
Solution: Allow UDP 1812, 1813Issue 2: Accounting Not Working
Symptoms:
✅ User connects successfully
❌ No accounting data in database
❌ Usage not trackedDiagnosis:
bash
# Check accounting table
mysql -u radius -p radius
SELECT * FROM radacct WHERE username='user001';
# Check RADIUS logs
grep Accounting /var/log/freeradius/radius.log
# Verify NAS sends accounting
# MikroTik: /radius monitor 0Common Causes:
1. Accounting not enabled on NAS
Solution: Enable accounting in NAS config
2. Wrong accounting port
Solution: Verify port 1813
3. Database connection issue
Solution: Check SQL module configuration
4. Interim-update not set
Solution: Set interim-update on NASIssue 3: CoA Not Working
Symptoms:
❌ Cannot disconnect user from Zal Ultra
❌ Bandwidth change not applied
❌ User stays connected after expiryDiagnosis:
bash
# Check CoA configuration
# MikroTik: /radius incoming print
# Test CoA manually
echo "User-Name=user001" | \
radclient 192.168.1.1:3799 disconnect YourSecretKey123
# Check firewall
iptables -L -n | grep 3799
# Check RADIUS logs
grep CoA /var/log/freeradius/radius.logCommon Causes:
1. CoA not enabled on NAS
Solution: Enable /radius incoming on MikroTik
2. Wrong CoA port
Solution: Verify port 3799
3. Firewall blocking
Solution: Allow UDP 3799
4. CoA secret mismatch
Solution: Verify secret matches
5. Wrong NAS IP in Zal Ultra
Solution: Check NAS IP in Zal Ultra matches actual NASBest Practices
Security
✅ Use strong RADIUS secrets (20+ characters)
✅ Restrict RADIUS access to NAS IPs only
✅ Use firewall rules (allow only UDP 1812, 1813, 3799)
✅ Enable RADIUS logging
✅ Monitor failed authentication attempts
✅ Regularly rotate RADIUS secrets
✅ Use encrypted connections (RadSec) if possible
✅ Limit database user permissions
✅ Regular security auditsPerformance
✅ Use connection pooling for database
✅ Optimize database queries (indexes)
✅ Monitor RADIUS response times
✅ Use appropriate interim-update interval (3-5 min)
✅ Clean old accounting records regularly
✅ Monitor server resources (CPU, RAM, disk)
✅ Use SSD for database storage
✅ Tune MySQL/MariaDB for performanceMonitoring
✅ Enable detailed logging
✅ Monitor authentication success/failure rate
✅ Track accounting packet loss
✅ Alert on RADIUS server down
✅ Monitor database size
✅ Track CoA success rate
✅ Review logs regularly
✅ Set up automated backupsRelated Documentation
- 📘 PPPoE Setup - PPPoE configuration
- 🌐 Hotspot Setup - Captive portal
- �� MikroTik API - API integration
Summary
✅ RADIUS Setup Complete!
What We Covered:
- ✅ MikroTik RADIUS configuration (image preserved)
- ✅ Zal Ultra built-in RADIUS
- ✅ FreeRADIUS installation and setup
- ✅ RADIUS attributes (standard + MikroTik VSA)
- ✅ CoA configuration
- ✅ Comprehensive troubleshooting
Key Points:
✅ RADIUS secret MUST match on both sides
✅ Use standard ports (1812, 1813, 3799)
✅ Enable CoA for remote management
✅ Set interim-update to 3-5 minutes
✅ Monitor RADIUS logs regularly
✅ Test thoroughly before production
✅ Implement security best practicesYour RADIUS server is ready for production! 🚀