Appearance
PPPoE Setup Guide
Overview
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) is the most widely used authentication method for ISPs worldwide. This comprehensive guide covers PPPoE setup for Zal Ultra with multiple network equipment vendors.
Supported Equipment:
- 🔧 MikroTik - RouterOS PPPoE Server
- 🌐 Cisco - IOS/IOS-XE Configuration
- 🔒 Juniper - JunOS PPPoE Setup
- 📡 vBNG & Bison BNG - Virtual BNG Solutions
What is PPPoE?
PPPoE = Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet
✅ Industry standard for ISP authentication
✅ Supports RADIUS AAA (Authentication, Authorization, Accounting)
✅ Dynamic IP assignment from pools
✅ Per-user bandwidth control
✅ Session management and accounting
✅ Compatible with all major routersHow PPPoE Works:
1. Subscriber connects PPPoE client
2. Router receives PPPoE discovery request
3. Router sends auth request to RADIUS (Zal Ultra)
4. Zal Ultra validates username/password
5. Zal Ultra sends IP, bandwidth, expiry to router
6. Router creates PPPoE session
7. Router sends accounting updates to Zal Ultra
8. Zal Ultra tracks data usage and quotaMikroTik PPPoE Setup
Architecture
Subscriber (PPPoE Client)
↓
MikroTik Router (PPPoE Server + RADIUS Client)
↓
Zal Ultra (RADIUS Server + Billing)Step 1: Create IP Pool
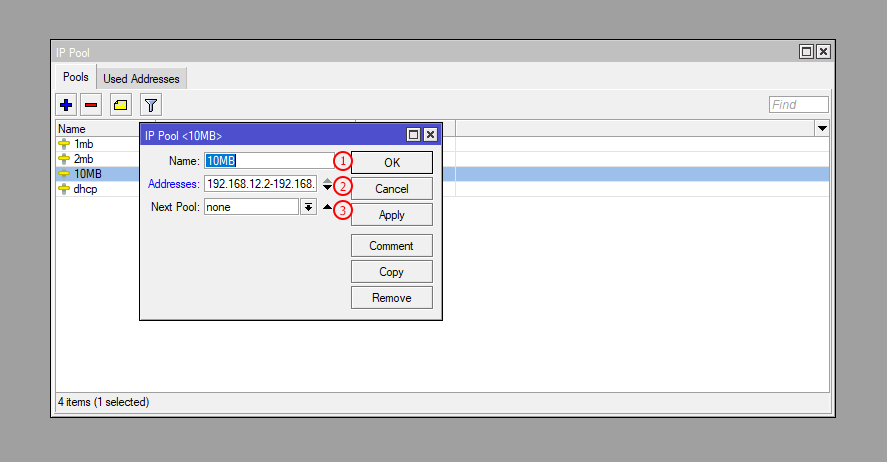
Most probably you already had IP Pools in your Mikrotik, if you don't have Pools then create IP Pools for PPPoE Profile. When a user will connect to the network he will get IP from these Pools.
| Number | Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Name | Enter the IP Pool Name (e.g., pppoe-pool-1) |
| 2 | Addresses | Enter the IP Pool Addresses (e.g., 10.10.1.2-10.10.1.254) |
| 3 | Next Pool | Select the Next Pool (optional, for pool chaining) |
CLI Command:
bash
/ip pool
add name=pppoe-pool-1 ranges=10.10.1.2-10.10.1.254
add name=pppoe-pool-2 ranges=10.10.2.2-10.10.2.254
add name=pppoe-pool-3 ranges=10.10.3.2-10.10.3.254Best Practices:
✅ Use private IP ranges (10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/12, 192.168.0.0/16)
✅ Reserve first 10 IPs for infrastructure (gateway, DNS, etc.)
✅ Create separate pools per interface/area for better management
✅ Use /24 or /23 subnets for easier troubleshooting
✅ Document pool assignments in your network diagram
✅ Leave room for growth (don't use all IPs)Pool Chaining Example:
bash
# Primary pool
/ip pool add name=pool-primary ranges=10.10.1.2-10.10.1.254
# Secondary pool (auto-used when primary is full)
/ip pool add name=pool-secondary ranges=10.10.2.2-10.10.2.254
# Link pools
/ip pool set pool-primary next-pool=pool-secondaryStep 2: Create PPPoE Profile
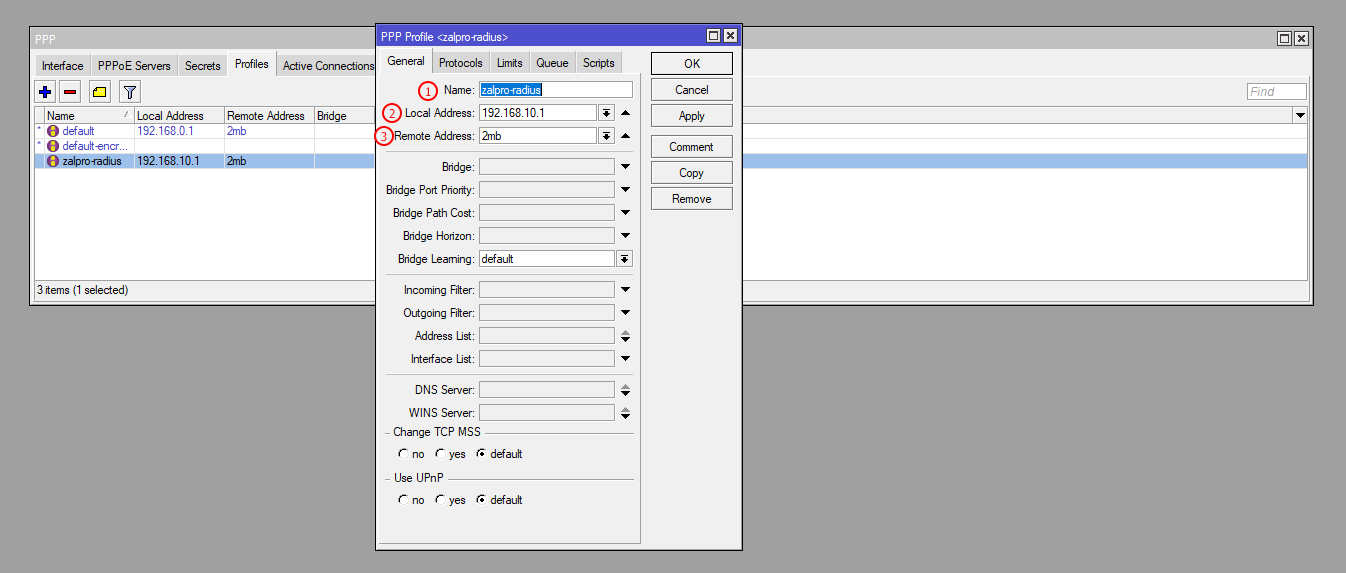
You need to create a PPPoE Profile for each and individual interface so that you can manage your users more effectively. In each interface, you need to select the respective PPPoE Profile, and in PPPoE Profile must set Local Address as interface gateway and Remote Address as Pool. Zal Ultra will override this Remote Address if you set Pool name in the Zal Ultra package.
| Number | Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Name | Enter the PPP profile Name (e.g., pppoe-profile-1) |
| 2 | Local Address | Enter the PPP profile Local Address (Gateway IP, e.g., 10.10.1.1) |
| 3 | Remote Address | Enter the PPP profile Remote Address (Pool name, e.g., pppoe-pool-1) |
CLI Command:
bash
/ppp profile
add name=pppoe-profile-1 \
local-address=10.10.1.1 \
remote-address=pppoe-pool-1 \
use-compression=no \
use-encryption=no \
use-mpls=no \
use-upnp=no \
only-one=yes \
change-tcp-mss=yes \
dns-server=8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4Profile Options Explained:
local-address=10.10.1.1 → Gateway IP for subscribers
remote-address=pool-name → IP pool for dynamic assignment
only-one=yes → Prevent duplicate logins (same user)
change-tcp-mss=yes → Fix MTU issues automatically
use-compression=no → Better performance (disable compression)
use-encryption=no → RADIUS handles security
dns-server=8.8.8.8 → DNS servers for clients
session-timeout=0 → No automatic disconnect
idle-timeout=0 → No idle disconnectMultiple Profiles Example:
bash
# Profile for Area A (10.10.1.0/24)
/ppp profile add name=area-a-profile \
local-address=10.10.1.1 \
remote-address=pppoe-pool-1 \
only-one=yes change-tcp-mss=yes
# Profile for Area B (10.10.2.0/24)
/ppp profile add name=area-b-profile \
local-address=10.10.2.1 \
remote-address=pppoe-pool-2 \
only-one=yes change-tcp-mss=yes
# Profile with custom DNS
/ppp profile add name=custom-dns-profile \
local-address=10.10.3.1 \
remote-address=pppoe-pool-3 \
dns-server=1.1.1.1,1.0.0.1 \
only-one=yes change-tcp-mss=yesStep 3: Create PPPoE Server
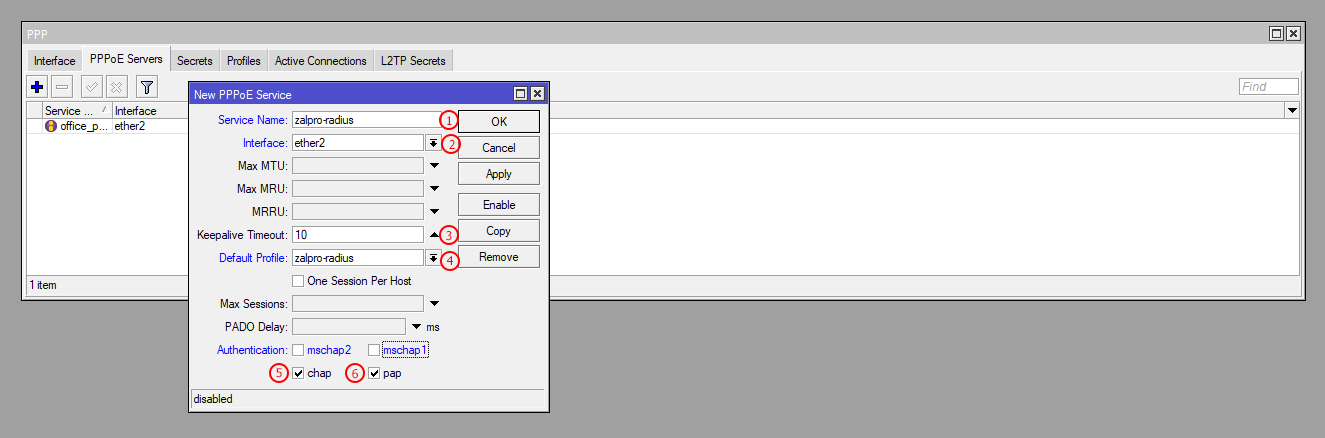
You need to create a PPPoE Server for each interface or for those interfaces which will be used for PPPoE user connection. You must select the correct PPPoE Profile from the dropdown. Each PPPoE Server should have a different PPPoE Profile. Make sure you select only CHAP and PAP authentication.
| Number | Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Service Name | Click on the PPPoE Servers (+)Plus button. Then enter the name of the service |
| 2 | Interface | Select the interface (e.g., ether2, bridge1) |
| 3 | Keepalive Timeout | Set the Keepalive Timeout to 10 seconds |
| 4 | Default Profile | Select the default profile name (e.g., pppoe-profile-1) |
| 5 | Chap | Select CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol) |
| 6 | Pap | Select PAP (Password Authentication Protocol) |
CLI Command:
bash
/interface pppoe-server server
add service-name=ISP-PPPoE \
interface=ether2 \
default-profile=pppoe-profile-1 \
authentication=pap,chap \
keepalive-timeout=10 \
max-mtu=1480 \
max-mru=1480 \
mrru=disabled \
one-session-per-host=yesAuthentication Methods:
PAP (Password Authentication Protocol):
✅ Simple plaintext password exchange
✅ Compatible with all PPPoE clients
✅ Zal Ultra can log passwords in login history
⚠️ Less secure (password sent in clear)
CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol):
✅ Encrypted password exchange (MD5 hash)
✅ More secure than PAP
✅ Prevents replay attacks
⚠️ Zal Ultra cannot see plaintext password
Recommendation: Enable BOTH (pap,chap) for maximum compatibility
Most clients will use CHAP if available, fallback to PAPMultiple Interface Setup:
bash
# Interface 1 - Area A (ether2)
/interface pppoe-server server
add service-name=Area-A-PPPoE \
interface=ether2 \
default-profile=area-a-profile \
authentication=pap,chap \
keepalive-timeout=10
# Interface 2 - Area B (ether3)
/interface pppoe-server server
add service-name=Area-B-PPPoE \
interface=ether3 \
default-profile=area-b-profile \
authentication=pap,chap \
keepalive-timeout=10
# Bridge Interface - Multiple VLANs
/interface pppoe-server server
add service-name=Bridge-PPPoE \
interface=bridge1 \
default-profile=pppoe-profile-1 \
authentication=pap,chap \
keepalive-timeout=10MTU/MRU Settings:
max-mtu=1480 → Maximum Transmission Unit
max-mru=1480 → Maximum Receive Unit
mrru=disabled → Disable multilink (not needed for PPPoE)
Why 1480?
Ethernet MTU: 1500 bytes
PPPoE Header: 8 bytes
PPP Header: 2 bytes
Overhead: 10 bytes total
Result: 1500 - 20 = 1480 bytes usableStep 4: Configure RADIUS AAA for PPPoE
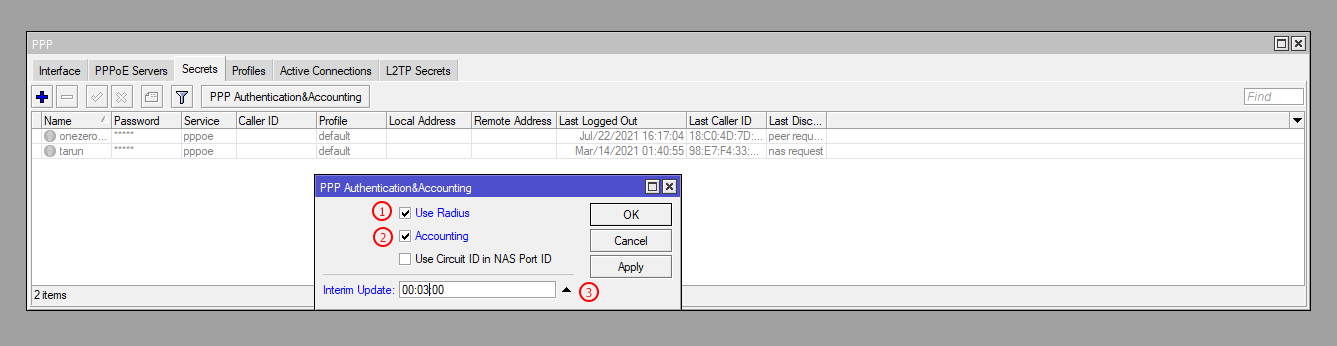
The most important part is enabling your PPPoE Servers for Radius and Radius Accounting (AAA). You can do that from PPPoE Authentication & Accounting section. Check Radius & Accounting options here. Don't forget to set the Accounting data sending time here which is 00:03:00 (3 Minutes). If you don't need to track data or accounting for data usage then ignore Interim Update time.
| Number | Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Use Radius | Check the Radius Box to enable RADIUS authentication |
| 2 | Accounting | Check the Accounting Box to enable RADIUS accounting |
| 3 | Interim Update | Set the Interim Update Time to a minimum of 3 minutes and a maximum of 15 minutes |
CLI Command:
bash
/ppp aaa
set accounting=yes \
interim-update=00:03:00 \
use-radius=yesAccounting Interim Update Explained:
Interim Update = How often MikroTik sends accounting data to Zal Ultra
3 minutes (00:03:00):
✅ Real-time data usage tracking
✅ Accurate quota management
✅ Quick disconnect on quota exceed
✅ Best for prepaid/quota-based plans
⚠️ Higher RADIUS server load
5 minutes (00:05:00):
✅ Balanced performance
✅ Good for most ISPs
✅ Moderate server load
✅ Recommended for medium networks
15 minutes (00:15:00):
✅ Lower server load
✅ Good for unlimited plans
⚠️ Delayed quota updates
⚠️ Less accurate real-time data
Recommendation: 3-5 minutes for quota-based, 10-15 for unlimitedComplete AAA Configuration:
bash
# Enable RADIUS AAA
/ppp aaa
set accounting=yes \
interim-update=00:03:00 \
use-radius=yes
# Verify configuration
/ppp aaa print
# Expected output:
# accounting: yes
# interim-update: 3m
# use-radius: yesStep 5: Configure RADIUS Server
Navigate to: Radius → Add RADIUS Server
CLI Command:
bash
/radius
add service=ppp \
address=192.168.1.100 \
secret=YourSecretKey123 \
authentication-port=1812 \
accounting-port=1813 \
timeout=3000ms \
src-address=192.168.1.1RADIUS Configuration Explained:
service=ppp → Use for PPP/PPPoE authentication
address=192.168.1.100 → Zal Ultra server IP
secret=YourSecretKey123 → Must match Zal Ultra NAS secret
authentication-port=1812 → Standard RADIUS auth port
accounting-port=1813 → Standard RADIUS accounting port
timeout=3000ms → 3 second timeout (recommended)
src-address=192.168.1.1 → MikroTik IP (optional but recommended)⚠️ CRITICAL: RADIUS Secret Must Match!
MikroTik RADIUS secret MUST match Zal Ultra NAS secret exactly!
If secrets don't match:
❌ Users cannot connect
❌ Authentication fails
❌ No error message to user
❌ RADIUS shows "Access-Reject"
Troubleshooting:
1. Check MikroTik: /radius print
2. Check Zal Ultra: Network → NAS → View NAS → Secret
3. Ensure both match exactly (case-sensitive)
4. Test with simple secret like "123456" first
5. Avoid special characters in secretStep 6: Enable CoA (Change of Authorization)
What is CoA?
CoA = Change of Authorization (RFC 5176)
Allows Zal Ultra to send commands to MikroTik:
✅ Disconnect user remotely
✅ Change bandwidth limits
✅ Update session attributes
✅ Force re-authenticationCLI Command:
bash
/radius incoming
set accept=yes port=3799CoA Configuration Explained:
accept=yes → Accept CoA requests from RADIUS
port=3799 → CoA port (must match Zal Ultra NAS settings)
When Zal Ultra needs to:
- Disconnect expired user → Sends CoA Disconnect
- Change bandwidth → Sends CoA with new rate-limit
- Update package → Sends CoA with new attributesVerify CoA:
bash
/radius incoming print
# Expected output:
# accept: yes
# port: 3799Complete MikroTik PPPoE Configuration Script
bash
# ============================================
# Complete MikroTik PPPoE Configuration
# For Zal Ultra RADIUS Integration
# ============================================
# Step 1: Create IP Pools
/ip pool
add name=pppoe-pool-1 ranges=10.10.1.2-10.10.1.254
add name=pppoe-pool-2 ranges=10.10.2.2-10.10.2.254
# Step 2: Create PPPoE Profiles
/ppp profile
add name=pppoe-profile-1 \
local-address=10.10.1.1 \
remote-address=pppoe-pool-1 \
use-compression=no \
use-encryption=no \
only-one=yes \
change-tcp-mss=yes \
dns-server=8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4
add name=pppoe-profile-2 \
local-address=10.10.2.1 \
remote-address=pppoe-pool-2 \
use-compression=no \
use-encryption=no \
only-one=yes \
change-tcp-mss=yes \
dns-server=8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4
# Step 3: Create PPPoE Servers
/interface pppoe-server server
add service-name=ISP-PPPoE-Area-A \
interface=ether2 \
default-profile=pppoe-profile-1 \
authentication=pap,chap \
keepalive-timeout=10 \
max-mtu=1480 \
max-mru=1480
add service-name=ISP-PPPoE-Area-B \
interface=ether3 \
default-profile=pppoe-profile-2 \
authentication=pap,chap \
keepalive-timeout=10 \
max-mtu=1480 \
max-mru=1480
# Step 4: Configure RADIUS Server (Zal Ultra)
/radius
add service=ppp \
address=192.168.1.100 \
secret=YourSecretKey123 \
authentication-port=1812 \
accounting-port=1813 \
timeout=3000ms \
src-address=192.168.1.1 \
comment="Zal Ultra RADIUS Server"
# Step 5: Enable RADIUS AAA
/ppp aaa
set accounting=yes \
interim-update=00:03:00 \
use-radius=yes
# Step 6: Enable CoA (Change of Authorization)
/radius incoming
set accept=yes port=3799
# Step 7: Configure Firewall (Allow Zal Ultra)
/ip firewall filter
add chain=input \
protocol=udp \
src-address=192.168.1.100 \
dst-port=1812,1813,3799 \
action=accept \
comment="Allow Zal Ultra RADIUS"
# Step 8: Verify Configuration
/ppp aaa print
/radius print
/radius incoming print
/interface pppoe-server server print
/ppp profile print
/ip pool printVerification & Testing
Check PPPoE Sessions
bash
# View all active PPPoE sessions
/interface pppoe-server print
# View detailed session info
/ppp active print detail
# Monitor new connections
/ppp active print follow
# Check specific user
/ppp active print where name=usernameCheck RADIUS Communication
bash
# View RADIUS statistics
/radius print stats
# Monitor RADIUS packets
/radius monitor 0
# Check incoming CoA
/radius incoming print statsCommon Verification Commands
bash
# Show IP pools usage
/ip pool used print
# Show PPP secrets (local, not RADIUS)
/ppp secret print
# Show PPPoE server status
/interface pppoe-server server print stats
# Show active sessions with details
/ppp active print detail where service=pppoe
# Show bandwidth usage
/interface pppoe-server monitor 0Troubleshooting
Issue 1: User Cannot Connect
Symptoms:
❌ PPPoE client shows "Authentication failed"
❌ No session created
❌ User sees "Error 691" or "Access Denied"Solutions:
bash
# 1. Check RADIUS secret
/radius print
# Verify secret matches Zal Ultra NAS secret
# 2. Check RADIUS server reachability
/tool ping 192.168.1.100 count=5
# 3. Check RADIUS communication
/radius monitor 0
# Should show "pending" or "accepted"
# 4. Check user credentials in Zal Ultra
# Network → Online Users → Search username
# 5. Check firewall
/ip firewall filter print where chain=input
# Ensure RADIUS ports (1812, 1813) are allowed
# 6. Enable debug logging
/system logging
add topics=radius action=memory
add topics=pppoe action=memory
# View logs
/log print where topics~"radius"
/log print where topics~"pppoe"Issue 2: User Connects But No Internet
Symptoms:
✅ PPPoE session created
✅ User gets IP address
❌ No internet access
❌ Cannot ping gatewaySolutions:
bash
# 1. Check user session
/ppp active print detail where name=username
# Verify IP address assigned
# 2. Check routing
/ip route print where dst-address=0.0.0.0/0
# Ensure default route exists
# 3. Check NAT
/ip firewall nat print where chain=srcnat
# Ensure masquerade rule exists
# 4. Check DNS
/ip dns print
# Ensure DNS servers configured
# 5. Test from MikroTik
/tool ping 8.8.8.8 source-address=10.10.1.2
# Use user's IP as sourceIssue 3: Accounting Not Working
Symptoms:
✅ User connects successfully
❌ No data usage shown in Zal Ultra
❌ Quota not decreasingSolutions:
bash
# 1. Check AAA settings
/ppp aaa print
# Ensure accounting=yes
# 2. Check interim update
/ppp aaa print
# Verify interim-update is set (e.g., 00:03:00)
# 3. Check RADIUS accounting
/radius print stats
# Look for accounting packets sent
# 4. Check Zal Ultra RADIUS logs
# Zal Ultra → System → RADIUS Logs
# Verify accounting packets received
# 5. Test accounting manually
/ppp active print detail
# Check "bytes-in" and "bytes-out" increasingIssue 4: CoA Not Working
Symptoms:
❌ Cannot disconnect user from Zal Ultra
❌ Bandwidth change not applied
❌ User stays connected after expirySolutions:
bash
# 1. Check CoA settings
/radius incoming print
# Ensure accept=yes and port=3799
# 2. Check firewall
/ip firewall filter print where chain=input
# Ensure port 3799 allowed from Zal Ultra
# 3. Check Zal Ultra NAS settings
# Network → NAS → Edit NAS
# Verify CoA port = 3799
# 4. Test CoA manually
# From Zal Ultra: Disconnect user
# Check MikroTik logs:
/log print where topics~"radius"Best Practices
Security
✅ Use strong RADIUS secret (20+ characters, mixed case, numbers)
✅ Restrict RADIUS access to Zal Ultra IP only
✅ Enable firewall rules for RADIUS ports
✅ Use only-one=yes to prevent duplicate logins
✅ Set keepalive-timeout to detect dead sessions
✅ Monitor failed authentication attempts
✅ Regularly review active sessionsPerformance
✅ Use interim-update=3-5 minutes for balance
✅ Disable compression (use-compression=no)
✅ Disable encryption (use-encryption=no)
✅ Enable change-tcp-mss=yes for MTU fix
✅ Use separate pools per interface
✅ Monitor RADIUS server load
✅ Use local fallback for critical usersMonitoring
✅ Set up logging for RADIUS and PPPoE
✅ Monitor active sessions count
✅ Track RADIUS response times
✅ Alert on RADIUS server down
✅ Monitor IP pool usage
✅ Track authentication failures
✅ Review CoA success rateNext Steps
For Other Vendors:
- 📘 Cisco PPPoE Setup - IOS/IOS-XE configuration
- 📗 Juniper PPPoE Setup - JunOS configuration
- 📙 vBNG & Bison BNG Setup - Virtual BNG solutions
Related Documentation:
- 🔐 RADIUS Setup - FreeRADIUS configuration
- 🌐 Hotspot Setup - Captive portal configuration
- 🔧 MikroTik API - API integration
Summary
✅ MikroTik PPPoE Setup Complete!
What We Configured:
- ✅ IP Pools for dynamic IP assignment
- ✅ PPPoE Profiles with gateway and DNS
- ✅ PPPoE Servers on interfaces
- ✅ RADIUS AAA for authentication & accounting
- ✅ CoA for remote disconnect & bandwidth control
- ✅ Firewall rules for security
Key Points:
✅ RADIUS secret MUST match Zal Ultra NAS secret
✅ Enable both PAP and CHAP for compatibility
✅ Set interim-update to 3-5 minutes
✅ Enable CoA for remote management
✅ Use only-one=yes to prevent duplicates
✅ Monitor RADIUS communication regularlyYour PPPoE network is now ready for Zal Ultra! 🚀