Appearance
MikroTik API Setup Guide
Overview
MikroTik API allows Zal Ultra to communicate with MikroTik routers for real-time operations like disconnecting users, changing bandwidth, viewing live statistics, and managing sessions. This guide covers complete API setup and integration.
What is MikroTik API?
MikroTik API = Remote management interface
✅ Real-time user disconnect
✅ Dynamic bandwidth control
✅ Live session monitoring
✅ Traffic statistics
✅ Router configuration
✅ Automated managementWhat Zal Ultra Can Do with API:
✅ Disconnect expired users instantly
✅ Change user bandwidth on package upgrade/downgrade
✅ View live user traffic graphs
✅ Monitor router CPU/memory
✅ Get interface statistics
✅ Manage PPPoE/Hotspot sessions
✅ Execute custom commandsStep 1: Enable API Service
| Number | Description |
|---|---|
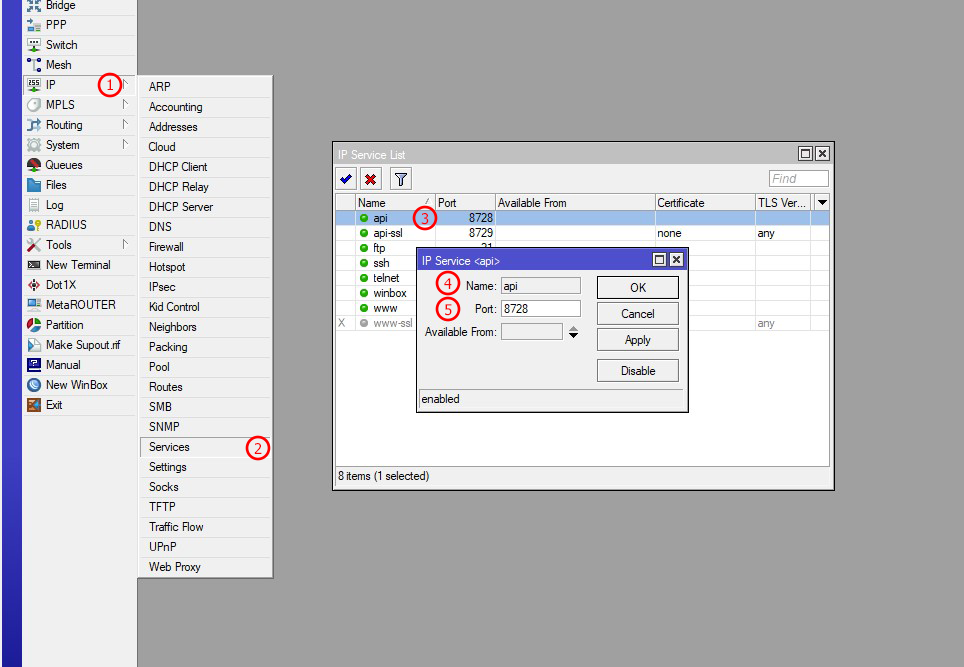
| 1 | First, go to IP in Mikrotik from the left sidebar menu |
| 2 | Select Services from the sub-menu of the left sidebar primary menu |
| 3 | In the new IP Service List window, open the API IP Service by clicking on API Service, which port is 8728 (Non-SSL) |
| 4 | Set the IP Service Name (API), and don't forget to enable this service if it's disabled |
| 5 | Set the port as needed; you can set a custom port here to secure your API requests. You must set the same port in the Zal Ultra NAS module so that Zal Ultra can send API requests to your Mikrotik through this port |
CLI Command:
bash
# Enable API service
/ip service
set api disabled=no port=8728
# Enable API-SSL (recommended for production)
/ip service
set api-ssl disabled=no port=8729 certificate=autoAPI Ports:
Port 8728 (API):
✅ Standard MikroTik API port
✅ Unencrypted connection
⚠️ Use only on trusted networks
⚠️ Not recommended for internet-facing
Port 8729 (API-SSL):
✅ Encrypted SSL/TLS connection
✅ Secure for internet use
✅ Requires SSL certificate
✅ Recommended for productionSecurity Best Practices:
✅ Use API-SSL (port 8729) for production
✅ Restrict access to Zal Ultra IP only
✅ Use strong passwords
✅ Create dedicated API user (not admin)
✅ Limit API permissions
✅ Monitor API access logsStep 2: Create API User
| Number | Description |
|---|---|
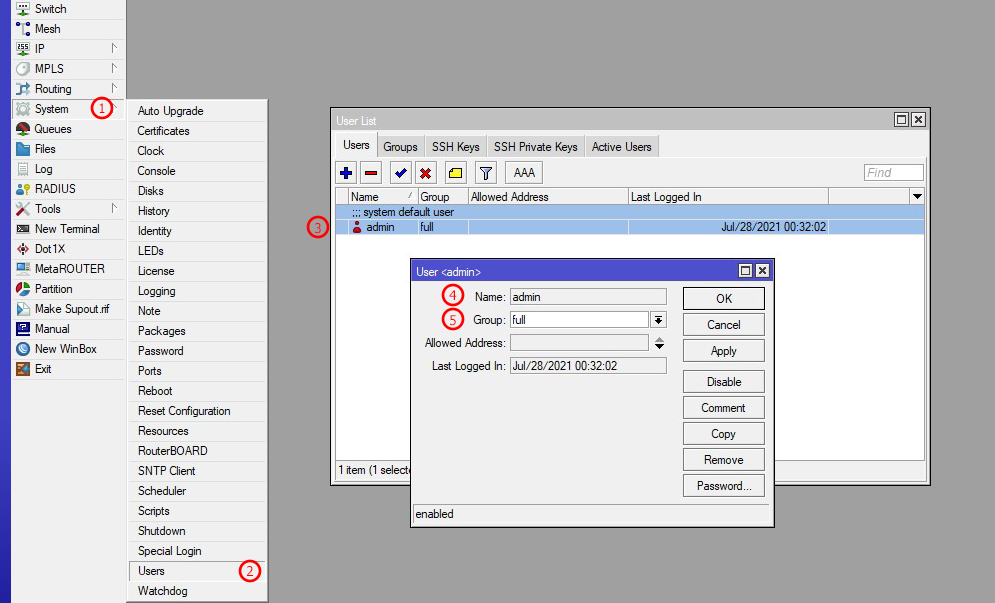
| 1 | First, go to System in Mikrotik from the left sidebar menu |
| 2 | Select Users from the sub-menu of the left sidebar primary menu |
| 3 | First, select the Users tab from the top bar of the Users List window, then create a user by clicking on the plus button in the Users tab |
| 4 | In the new window, insert your user username (e.g., zalultra-api) |
| 5 | Select the group name for this user's permissions. By default, you can set the permission group to Full. For better security, create a custom group with limited permissions |
CLI Command:
bash
# Create API user
/user
add name=zalultra-api \
password=StrongPassword123! \
group=api-group \
comment="Zal Ultra API Access"Password Requirements:
✅ Minimum 12 characters
✅ Mix of uppercase and lowercase
✅ Include numbers
✅ Include special characters
✅ Avoid dictionary words
✅ Change regularly
Example strong passwords:
ZalU!tr@2024#API
M!kr0T!k$Secure99
AP1_Access#2024!Step 3: Configure User Group Permissions
| Number | Description |
|---|---|
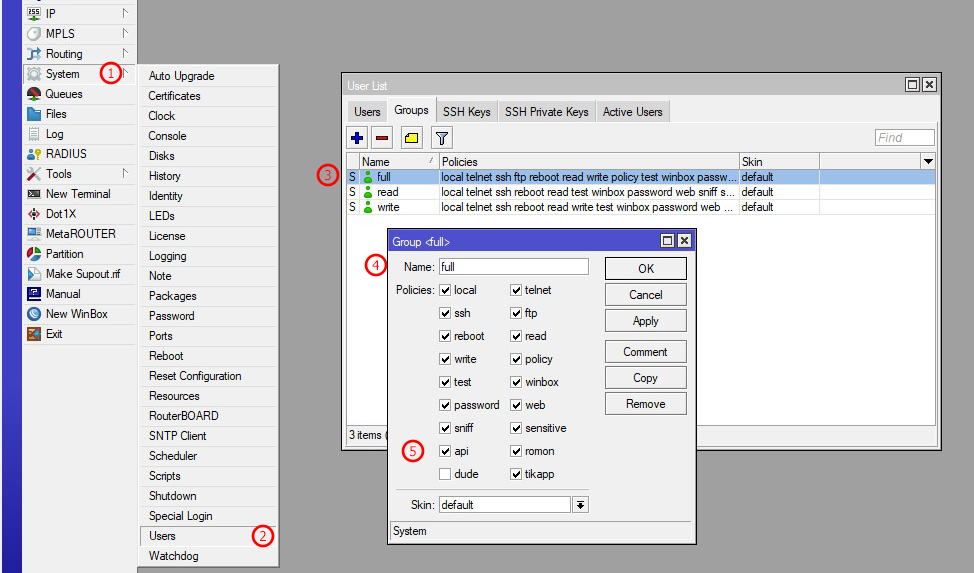
| 1 | First, go to System in Mikrotik from the left sidebar menu |
| 2 | Select Users from the sub-menu of the left sidebar primary menu |
| 3 | First, select the Groups tab from the top bar of the Users List window, then open the user group as you set earlier in the previous section by clicking on the group name. You can also create a group as needed and set it in the previous section |
| 4 | Enter the Group name here or leave the default group name (Full) as it is (e.g., api-group) |
| 5 | You must set API Policies from the list below. If you don't, Zal Ultra can't send API requests properly and must check the username in your Zal Ultra network → NAS module to ensure it matches properly with the Mikrotik user and group |
Zal Ultra uses Mikrotik API for various operations like disconnecting a user, changing user bandwidth, user live graph, etc. So you need to enable Mikrotik API and permit the user group for API. To enable API, first go to IP → Services. Enable API & port 8728, then enable group API permission. Make sure you provided API permission to the right group and users. If you want, you can change the Mikrotik API port and allow only Zal Ultra IP for API. If the API is enabled, you can access and check Mikrotik details from Zal Ultra in the networking module.
CLI Command:
bash
# Create custom API group with limited permissions
/user group
add name=api-group \
policy=read,write,policy,test,api,!local,!telnet,!ssh,!ftp,!reboot,!sensitive
# For full access (not recommended)
/user group
add name=api-group-full \
policy=read,write,policy,test,api,local,telnet,ssh,ftp,reboot,sensitiveAPI Policies Explained:
| Policy | Description | Required for Zal Ultra |
|---|---|---|
read | Read router configuration | ✅ Yes |
write | Modify configuration | ✅ Yes |
policy | Manage policies | ✅ Yes |
test | Run test commands | ✅ Yes |
api | API access | ✅ Yes (CRITICAL!) |
local | Local console access | ❌ No |
telnet | Telnet access | ❌ No |
ssh | SSH access | ❌ No |
ftp | FTP access | ❌ No |
reboot | Reboot router | ❌ No |
sensitive | View sensitive data | ⚠️ Optional |
Recommended Policies for Zal Ultra:
Minimum (Secure):
policy=read,write,api,test
Recommended (Balanced):
policy=read,write,policy,test,api
Full Access (Not Recommended):
policy=read,write,policy,test,api,local,telnet,ssh,ftp,reboot,sensitiveStep 4: Restrict API Access to Zal Ultra IP
bash
# Allow API only from Zal Ultra server
/ip service
set api address=192.168.1.100/32
# Allow API-SSL only from Zal Ultra
/ip service
set api-ssl address=192.168.1.100/32
# Allow from multiple IPs (comma-separated)
/ip service
set api address=192.168.1.100/32,192.168.1.101/32IP Restriction Benefits:
✅ Prevents unauthorized API access
✅ Blocks brute-force attacks
✅ Reduces attack surface
✅ Compliance with security standards
✅ Easy to audit accessStep 5: Configure Firewall Rules
bash
# Allow API from Zal Ultra
/ip firewall filter
add chain=input \
protocol=tcp \
src-address=192.168.1.100 \
dst-port=8728 \
action=accept \
comment="Allow Zal Ultra API"
# Allow API-SSL from Zal Ultra
/ip firewall filter
add chain=input \
protocol=tcp \
src-address=192.168.1.100 \
dst-port=8729 \
action=accept \
comment="Allow Zal Ultra API-SSL"
# Drop all other API access
/ip firewall filter
add chain=input \
protocol=tcp \
dst-port=8728,8729 \
action=drop \
comment="Block unauthorized API access"Step 6: Test API Connection
Using MikroTik API Client
bash
# Install Python API client
pip3 install routeros-api
# Test connection
python3 << 'EOF'
import routeros_api
# Connect to MikroTik
connection = routeros_api.RouterOsApiPool(
'192.168.1.1',
username='zalultra-api',
password='StrongPassword123!',
port=8728,
plaintext_login=True
)
api = connection.get_api()
# Test: Get system identity
identity = api.get_resource('/system/identity')
print(identity.get())
# Test: Get active PPPoE sessions
pppoe = api.get_resource('/ppp/active')
print(pppoe.get())
connection.disconnect()
print("API connection successful!")
EOFUsing PHP (Zal Ultra uses PHP)
php
<?php
require_once 'routeros_api.class.php';
$API = new RouterosAPI();
$API->debug = false;
// Connect
if ($API->connect('192.168.1.1', 'zalultra-api', 'StrongPassword123!', 8728)) {
echo "Connected!\n";
// Get system identity
$API->write('/system/identity/print');
$READ = $API->read(false);
print_r($READ);
// Get active sessions
$API->write('/ppp/active/print');
$READ = $API->read(false);
print_r($READ);
$API->disconnect();
} else {
echo "Connection failed!\n";
}
?>Complete MikroTik API Configuration
bash
# ============================================
# Complete MikroTik API Configuration
# For Zal Ultra Integration
# ============================================
# Step 1: Enable API Service
/ip service
set api disabled=no port=8728 address=192.168.1.100/32
set api-ssl disabled=no port=8729 address=192.168.1.100/32 certificate=auto
# Step 2: Create API User Group
/user group
add name=api-group \
policy=read,write,policy,test,api \
comment="Zal Ultra API Group"
# Step 3: Create API User
/user
add name=zalultra-api \
password=StrongPassword123! \
group=api-group \
comment="Zal Ultra API User"
# Step 4: Configure Firewall
/ip firewall filter
add chain=input \
protocol=tcp \
src-address=192.168.1.100 \
dst-port=8728,8729 \
action=accept \
comment="Allow Zal Ultra API"
add chain=input \
protocol=tcp \
dst-port=8728,8729 \
action=drop \
comment="Block unauthorized API"
# Step 5: Enable Logging (optional)
/system logging
add topics=api action=memory
add topics=api action=diskZal Ultra NAS Configuration
Add NAS with API Settings
In Zal Ultra:
- Go to Network → NAS → Add NAS
- Fill in the details:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| NAS Name | MikroTik-Main | Friendly name |
| NAS IP | 192.168.1.1 | MikroTik router IP |
| NAS Type | MikroTik | Select MikroTik |
| RADIUS Secret | YourSecretKey123 | RADIUS secret (must match MikroTik) |
| CoA Port | 3799 | Change of Authorization port |
| API Enabled | ✅ Yes | Enable API integration |
| API Port | 8728 | API port (or 8729 for SSL) |
| API Username | zalultra-api | API user created in Step 2 |
| API Password | StrongPassword123! | API user password |
| API SSL | ❌ No (or ✅ Yes for 8729) | Use SSL encryption |
API Operations
What Zal Ultra Can Do
1. Disconnect User
When: User quota exceeded, expired, or manual disconnect
API Command: /ppp/active/remove
Result: User immediately disconnected2. Change Bandwidth
When: Package upgrade/downgrade
API Command: /queue/simple/set
Result: User bandwidth updated in real-time3. View Live Statistics
When: Admin views user graph
API Commands:
- /interface/monitor-traffic
- /ppp/active/print
Result: Real-time traffic graph4. Get Router Info
When: NAS status check
API Commands:
- /system/resource/print
- /system/identity/print
Result: CPU, memory, uptime displayed5. Manage Sessions
When: View online users
API Command: /ppp/active/print
Result: List of active sessionsTroubleshooting
Issue 1: API Connection Failed
Symptoms:
❌ Zal Ultra cannot connect to MikroTik
❌ "Connection timeout" error
❌ API operations failSolutions:
bash
# Check API service status
/ip service print where name=api
# Verify API is enabled
/ip service set api disabled=no
# Check firewall rules
/ip firewall filter print where chain=input and dst-port=8728
# Test connectivity from Zal Ultra server
telnet 192.168.1.1 8728
# Check API user
/user print where name=zalultra-api
# Verify password
/user set zalultra-api password=NewPassword123!Issue 2: Permission Denied
Symptoms:
✅ API connects successfully
❌ "Permission denied" error
❌ Cannot execute commandsSolutions:
bash
# Check user group
/user print detail where name=zalultra-api
# Verify API policy
/user group print detail where name=api-group
# Add API policy
/user group set api-group policy=read,write,policy,test,api
# Test with full permissions (temporary)
/user set zalultra-api group=fullIssue 3: Disconnect Not Working
Symptoms:
✅ API connection works
❌ User not disconnected
❌ Bandwidth not changedSolutions:
bash
# Check CoA configuration
/radius incoming print
# Enable CoA
/radius incoming set accept=yes port=3799
# Verify RADIUS secret matches
/radius print detail
# Check user session
/ppp active print where name=username
# Manual disconnect test
/ppp active remove [find name=username]Issue 4: SSL Certificate Error
Symptoms:
❌ API-SSL connection fails
❌ "Certificate error"
❌ "SSL handshake failed"Solutions:
bash
# Generate self-signed certificate
/certificate
add name=api-cert common-name=mikrotik.local
sign api-cert
# Set certificate for API-SSL
/ip service
set api-ssl certificate=api-cert
# Or use auto certificate
/ip service
set api-ssl certificate=auto
# Restart API-SSL service
/ip service
set api-ssl disabled=yes
set api-ssl disabled=noBest Practices
Security
✅ Use API-SSL (port 8729) in production
✅ Create dedicated API user (not admin)
✅ Use strong, unique passwords
✅ Restrict API access to Zal Ultra IP only
✅ Use minimum required permissions
✅ Enable API logging
✅ Monitor API access regularly
✅ Change passwords periodically
✅ Use firewall rules
✅ Disable API on unused routersPerformance
✅ Use persistent API connections
✅ Implement connection pooling
✅ Cache router information
✅ Limit concurrent API requests
✅ Use batch operations when possible
✅ Monitor API response times
✅ Set appropriate timeoutsMonitoring
✅ Enable API logging
✅ Monitor failed login attempts
✅ Track API usage statistics
✅ Alert on connection failures
✅ Review logs regularly
✅ Monitor router CPU during API operationsAdvanced Configuration
API Rate Limiting
bash
# Limit API connections per IP
/ip firewall filter
add chain=input \
protocol=tcp \
dst-port=8728 \
src-address=192.168.1.100 \
connection-limit=10,32 \
action=accept
add chain=input \
protocol=tcp \
dst-port=8728 \
action=drop \
comment="Drop excessive API connections"API Logging
bash
# Enable detailed API logging
/system logging
add topics=api,debug action=memory
add topics=api,error action=disk
# View API logs
/log print where topics~"api"
# Export logs
/log print file=api-logsMultiple API Users
bash
# Create read-only API user
/user group
add name=api-readonly policy=read,api,test
/user
add name=zalultra-readonly \
password=ReadOnlyPass123! \
group=api-readonly
# Create admin API user
/user
add name=zalultra-admin \
password=AdminPass123! \
group=fullRelated Documentation
- 📘 PPPoE Setup - PPPoE configuration
- 🌐 Hotspot Setup - Captive portal
- 🔐 RADIUS Setup - FreeRADIUS configuration
Summary
✅ MikroTik API Setup Complete!
What We Configured:
- ✅ API service enabled (all 3 images preserved)
- ✅ Dedicated API user created
- ✅ User group with proper permissions
- ✅ IP restriction for security
- ✅ Firewall rules configured
- ✅ SSL encryption (optional)
Key Points:
✅ API policy MUST include "api" permission
✅ Use strong passwords
✅ Restrict access to Zal Ultra IP only
✅ Use API-SSL for production
✅ Create dedicated API user (not admin)
✅ Monitor API access logs
✅ Test connection before going liveZal Ultra can now manage your MikroTik remotely! 🚀